Research
periDEM
Granular media
As part of a research initiative to understand granular media, the effect of particle shapes on the mechanical response of the aggregate has been studied, capturing the damage of individual grains using peridynamics. Regarding the work on 3D simulations, three-dimensional axisymmetric problems have been considered, where the geometry and deformation fields are symmetric about an axis. This is an important class of problems in solid mechanics where the symmetry can be exploited to reduce computational cost.
A two-dimensional model that exactly represents the full 3D axisymmetric linear peridynamic model has been derived by incorporating out-of-plane bond forces into the representative 2D plane. This approach allows for a substantial reduction in the computational cost compared to the full 3D simulation.
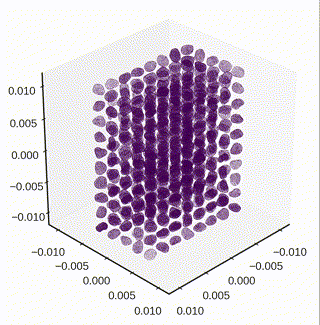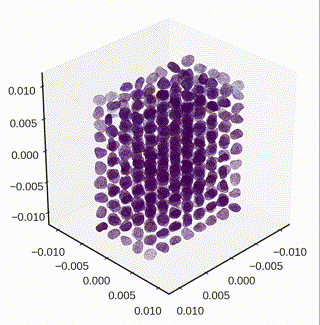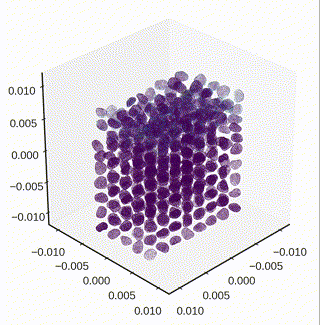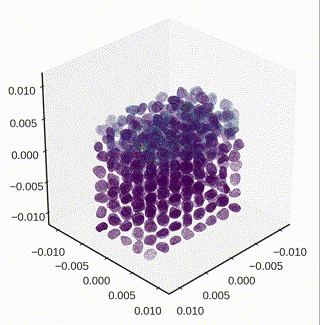
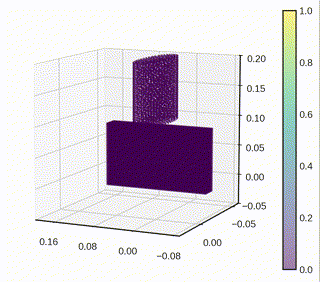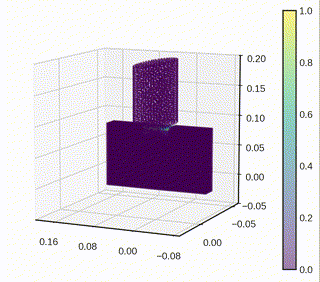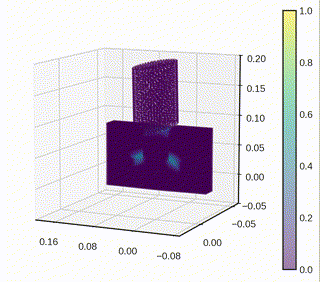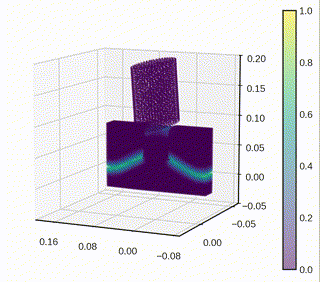
Settling down particles under gravity
- The dynamic settling of particle
Mechanic of fracture
iThe classical approach to studying solid material deformation treats materials as a continuum, modeling displacements using the Cauchy Momentum equation. However, this fails to capture material behavior when deformation fields are non-differentiable, such as at fracture points. Peridynamics, introduced by Stewart Silling in 2000, addresses this limitation by modeling material points as interacting via bond forces and using an integral equation, accommodating discontinuous deformations like cracks. Peridynamics has been used to model crack formation and branching in various fracture problems.
Quantitative finance
Structral models for credit risk and option pricing
Fractional models
comming soon!!!
L'evy processes
I am also interested in the application of the L'evy process in finance. In this area, my early work received fair attention in the field by researchers where I developed a meshfree radial basis function for solving the problem of American option pricing under jump-diffusion regime-switching model for the first time. Besides, I also developed the structural risk modeling under the jump-diffusion regime-switching model with the synchronous jump to use tempered stable L'evy processes and proposed a new meshfree collocation method to desingularize the problem and solve it efficiently here.
Over the recent years, we witness the success of regime-switching models (or Markov-modulated) in the field of quantitative finance. These models can capture the observed behavior of financial time series in a precise way. A straightforward approach to introduce “regime change” into the model is to assume that the dynamics of the underlying financial asset is governed by a L'evy process whose parameters are dependent on the states of a continuous-time hidden Markov chain with states describing the regimes in which the financial or economic system operates. Indeed, these models benefit from realistic assumptions such that they can replicate the important features of the market like volatility smiles, skewness, and term structure premiums by employing these models.
Numerical analysis
Galerkin methods
DPG method
In the area of numerical solutions of differential equations, I am particularly interested in the Discontinuous Petrov Galerkin method. In my research, I tried to employ this method for the first time in the quantitative finance field for valuing options including the vanilla option, American option, and exotic options such as the Asian option, the double barrier option. Besides, I used this method to analyze the fourth-order partial differential equation (Biharmonic PDE) arisen from the mechanics of the materials field. I am also working on analyzing the more complex PDEs and PIDEs from quantitative finance and topology optimization with the DPG method such as financial modeling under jump-diffusion model, as well as Hamilton Jacobi equation. To be more specific I briefly recall the DPG method with the optimal test space in the following. here
C0 Interiour penalty method
- comming soon
Variational inequlities
In the area of variational inequality, I am interested in their applications both in plasticity problems and the American option pricing and their numerical methods. I am also interested in the design optimization of problems formulated with variational inequalities. It is natural to study the nature of this family of the variational problem first here.
Stocahstic differential equation
I am also interested in the stochastic differential equation and Malliavin calculus. My research when I was a master’s student was the numerical solution of stochastic differential equations with multi-point boundary value problems SBVPs. These families of SDEs have a broad application such as smoothing, maximum a posteriori estimation of trajectories of diffusions, wave motion in random media, stochastic optimal control, valuation of boundary-linked assets, and in the study of reciprocal processes. They also arise from the semi-discretization by Rothe’s method of stochastic partial differential equations that is another field that I have an interest in it. Indeed, we are interested in the numerical solution of SBVPs of the form
